Ivezić et al. 1997 present a 1D continuum radiative transfer benchmark problem consisting of a star embedded in a spherical dust shell with an inner cavity free of dust. Scattering is taken to be isotropic and dust emission is calculated assuming conditions of local thermal equilibrium (LTE) with the radiation field. The authors provide results produced by several radiative transfer codes for two dust density profiles and for optical depths ranging from 1 to 1000.
| Publication | Ivezić et al. 1997 [ADS] |
|---|---|
| Ski file | ivezic_template.ski |
The figures below show the temperature profiles (left column) and normalized SEDs (right column) produced by SKIRT for this benchmark. The top row shows results for the constant density profile; the bottom row for the more challenging \(\rho(r)\propto\,r^{-2}\) profile. Each panel shows the solutions for the different optical depths as indicated in the legend. The dashed curves in the right column indicate the reference SEDs taken from the benchmark FTP site. The SKIRT results match the benchmark results well, except for the case with steep density gradient and very high optical depth, which is not shown.
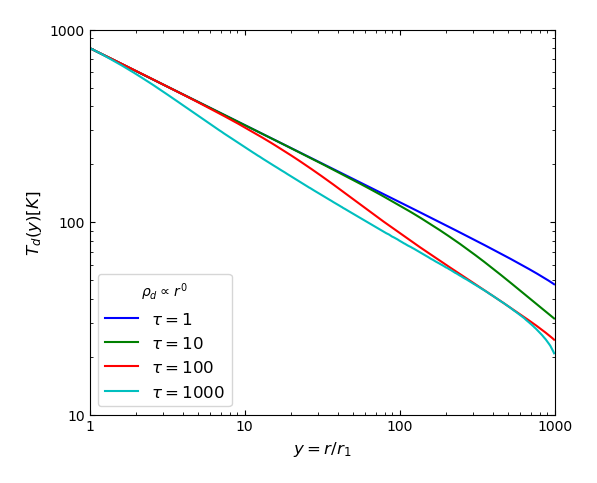 | 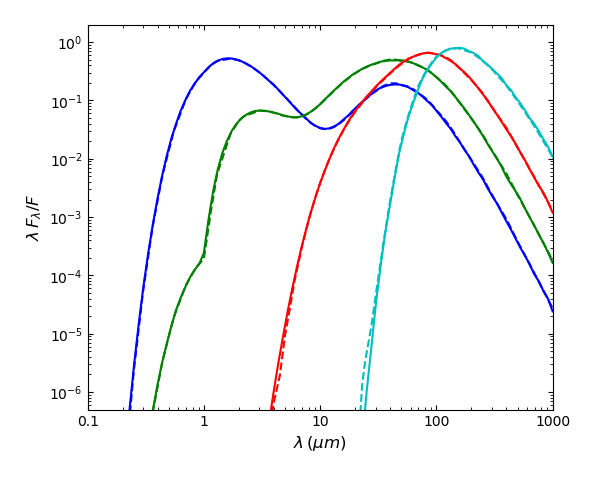 |
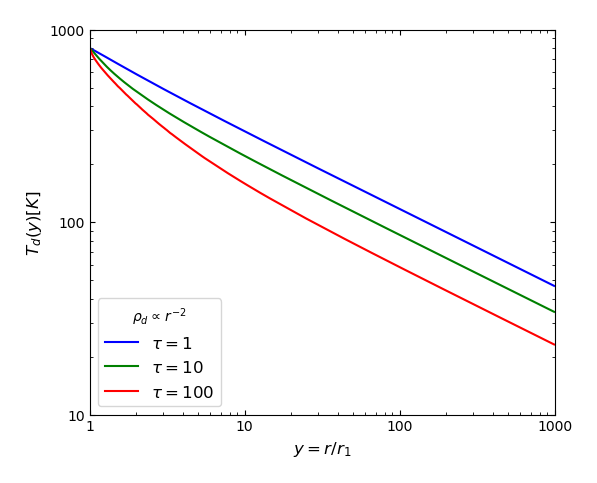 | 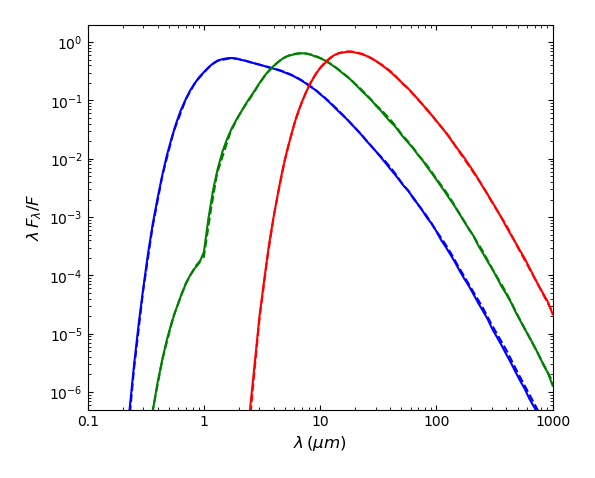 |
To perform this benchmark, download the ski file provided above (References and downloads). Open the ski file in a text editor to adjust the following parameter values to a particular benchmark configuration:
| Parameter | XML element | XML attribute |
|---|---|---|
| Density exponent | ShellGeometry | exponent |
| Optical depth | OpticalDepthMaterialNormalization | opticalDepth |
| Source luminosity | IntegratedLuminosityNormalization | integratedLuminosity |
The benchmark specifies radial optical depth values (integrated from the origin to infinity) while the values in the ski file normalize the optical depth along the complete X-axis (integrated from negative to positive infinity). The value in the ski file therefore must be set to twice the value specified for the corresponding benchmark.
The source luminosity must be adjusted to ensure that the dust temperature at the inner shell boundary is 800 K for each configuration as required by the benchmark definition. With the length scales adopted in the ski file provided above, the appropriate values are:
| Density exponent | Radial optical depth | Source luminosity ( \(\text{L}_\odot\)) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 23.6 |
| 0 | 10 | 23.5 |
| 0 | 100 | 22.8 |
| 0 | 1000 | 18.7 |
| 2 | 1 | 20.2 |
| 2 | 10 | 13.1 |
| 2 | 100 | 5.8 |
| 2 | 1000 | — |
Then pass the (name of) the ski file to SKIRT as a single command line argument. Higher optical depths and steeper dust density gradients lead to longer simulation run times. At the end of the simulation run, SKIRT outputs temperature profiles and SEDs which can be compared to the original benchmark results.